The semiconductor industry, a formidable force propelling technological progress across numerous sectors, stands at a crucial juncture. Every top semiconductor company is constantly pushing the boundaries of chip design and fabrication (commonly referred to as “fab”). However, a complex web of regulations continuously challenges this relentless pursuit of innovation. Understanding and navigating these regulations is crucial for any semiconductors company, big or small, to ensure continued growth and a role in shaping the future.
This article will examine the intricate landscape of semiconductor regulations, analyzing both the challenges they pose and the opportunities they offer. The discussion will encompass the primary areas of regulatory emphasis, the ramifications for various industry participants (ranging from major semiconductor companies to smaller design enterprises), as well as strategies for effectively navigating this intricate terrain.
The Engine of Progress: Why Regulations Matter
Semiconductors are tiny, intricate components that power everything from smartphones and laptops to medical equipment and self-driving cars. As chip designs become more intricate using ever-shrinking transistors (measured in nanometers!), the potential environmental and safety risks associated with their production also rise. Here’s where regulations come in:
Get in touch
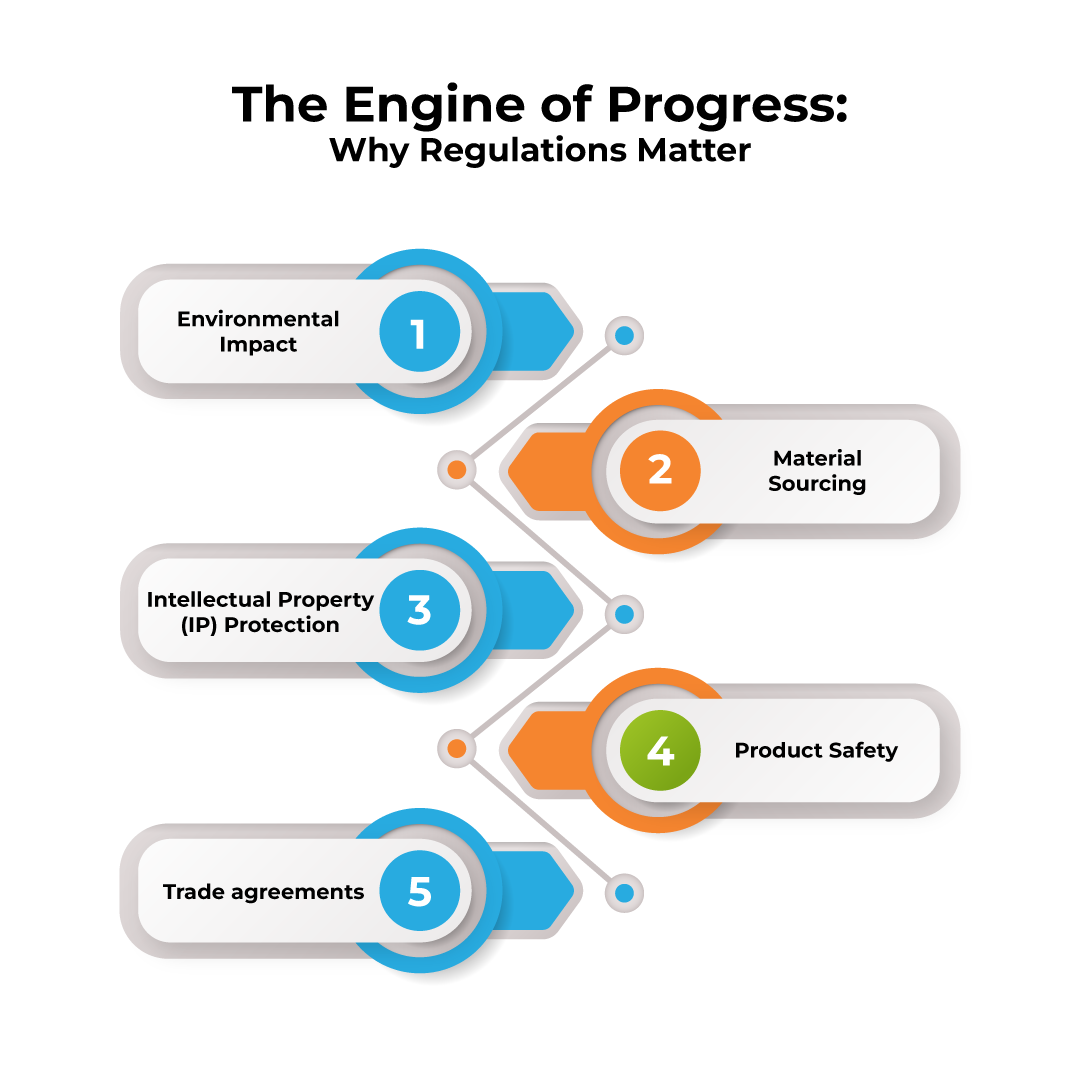
- Environmental Impact: Manufacturing processes can generate hazardous waste and consume significant energy. Regulations ensure responsible disposal of waste and promote energy-efficient production practices.
- Material Sourcing: The rare earth elements and other materials used in chip production can be ethically and environmentally problematic if sourced from conflict zones. Regulations aim to ensure ethical sourcing practices.
- Intellectual Property (IP) Protection: The intense competition in the industry necessitates robust IP protection to incentivize research and development (R&D). Regulations safeguard innovations and prevent unauthorized copying.
- Product Safety: Chip malfunctions can have serious consequences, especially in safety-critical applications like medical devices and autonomous vehicles. Regulations define rigorous testing and certification procedures.
- Trade agreements: International trade agreements can impact the cost and availability of raw materials and finished products. Understanding these agreements is vital for semiconductors companies operating in a globalized market.
These are just some examples, and the specific regulations a semiconductor company encounters will vary depending on its location, the type of chips it produces, and its target markets.
Challenges
- Compliance Costs: Implementing and maintaining compliance with regulations can be a significant expense. This can be particularly burdensome for a smaller semiconductor design company that may not have the resources of larger fabs.
- Market Access Delays: Navigating complex export control procedures can delay the entry of new technologies into specific markets.
- Innovation Stifling: Overly restrictive regulations can inadvertently hinder innovation by limiting access to essential materials or technologies.
- Talent Gap: Understanding and navigating regulations requires specialized expertise in semiconductor engineering, legal matters, and international trade. There is often a shortage of professionals with this skill set.
Opportunities
- Competitive Advantage: Companies with a strong grasp of regulations can gain a competitive advantage by ensuring their products comply with all relevant standards, positioning them as trustworthy partners.
- Market Leadership: Semiconductor companies can proactively shape future regulations by engaging with policymakers and advocating for policies that support responsible innovation and fair trade practices.
- Sustainability Focus: Stringent environmental regulations can act as a catalyst for developing innovative and sustainable manufacturing practices.
Strategies for Navigating Complex Regulations
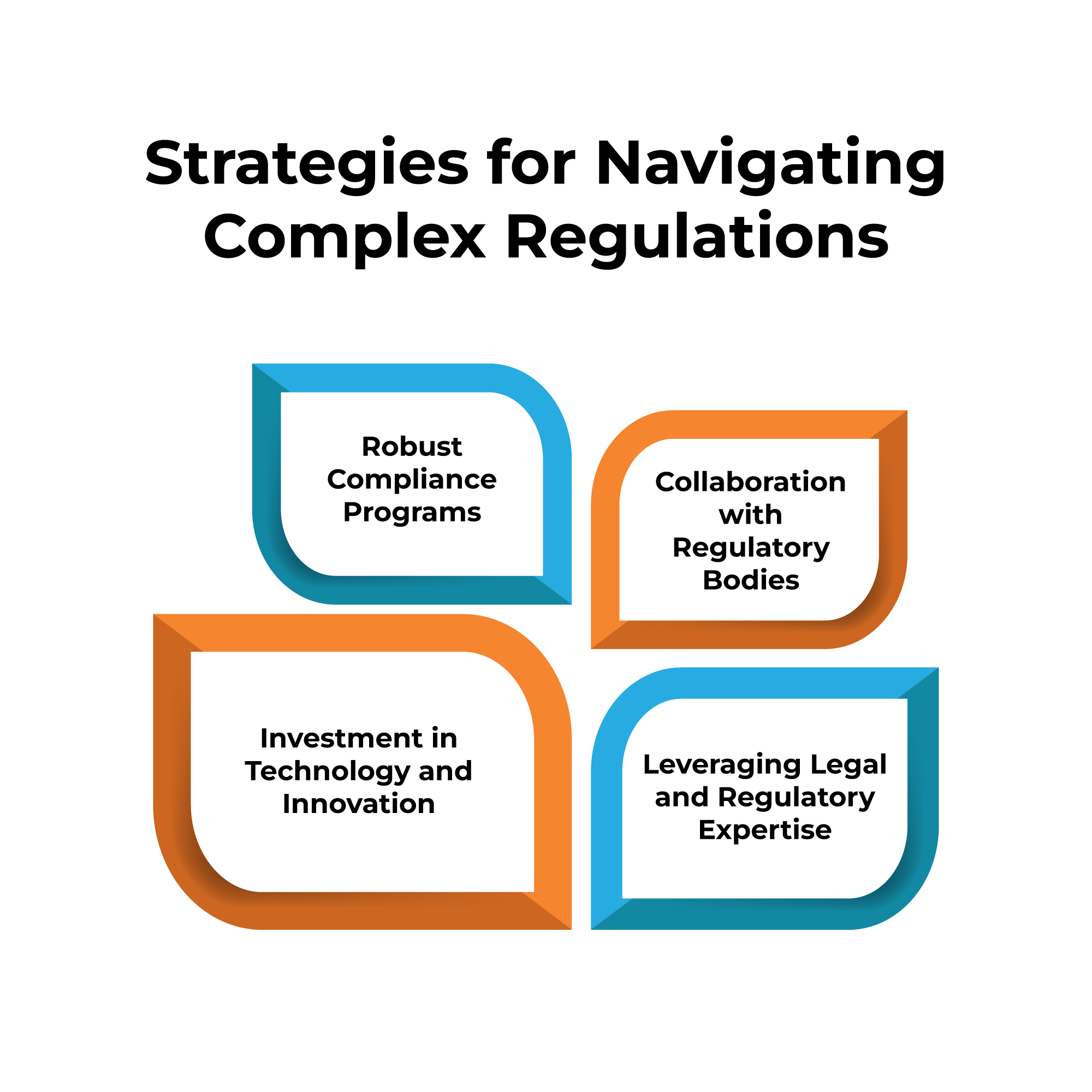
Robust Compliance Programs
To effectively navigate the complex regulatory landscape, semiconductor companies need to establish robust compliance programs. These programs should include comprehensive training for employees, regular audits, and a clear understanding of relevant regulations. By fostering a culture of compliance, companies can minimize the risk of violations and ensure smooth operations.
For example, a top semiconductor company might involve a dedicated compliance team responsible for monitoring changes in regulations, conducting internal reviews, and ensuring that all departments adhere to legal requirements. This proactive approach helps identify potential issues early and address them before they escalate.
Collaboration with Regulatory Bodies
Engaging with regulatory bodies can also be beneficial. By participating in industry groups and working closely with regulators, semiconductor companies can gain insights into upcoming regulatory changes and provide feedback on proposed rules. This collaboration can help shape regulations in a way that balances industry needs with governmental objectives.
Investment in Technology and Innovation
Investing in technology and innovation is another key strategy for navigating regulations. Advanced technologies can help semiconductor companies meet regulatory requirements more efficiently. For instance, innovations in green manufacturing techniques can reduce environmental impact, while advanced encryption technologies can enhance data protection and cybersecurity.
The biggest semiconductor company often leads the way in adopting such innovations. By staying at the forefront of technological advancements, these companies can not only comply with current regulations but also anticipate future regulatory trends.
Leveraging Legal and Regulatory Expertise
Investing in technology and innovation is another key strategy for navigating regulations. Advanced technologies can help semiconductor companies meet regulatory requirements more efficiently. For instance, innovations in green manufacturing techniques can reduce environmental impact, while advanced encryption technologies can enhance data protection and cybersecurity.
The biggest semiconductor company often leads the way in adopting such innovations. By staying at the forefront of technological advancements, these companies can not only comply with current regulations but also anticipate future regulatory trends.
The Future of Regulation in the Semiconductor Industry
As technology advances, the semiconductor industry’s regulatory landscape is likely to become even more complex. Emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI), the Internet of Things (IoT), and 5G will introduce new regulatory challenges related to data security, privacy, and cross-border data flows.
To stay ahead, semiconductor companies must remain agile and adaptable. This involves continuously monitoring regulatory developments, investing in compliance and innovation, and fostering a collaborative approach with regulators and industry peers. By doing so, they can not only navigate the current regulatory landscape but also shape the future of the industry.
Also Read : The Impact of 5G Technology on the Future of Embedded Systems
Let’s Sum Up
The semiconductor industry is positioned at the vanguard of technological advancement. As the industry undergoes transformation, regulatory measures will play a pivotal role in shaping its trajectory. Through proactive engagement with policymakers, adoption of a forward-looking compliance stance, and promotion of collaborative efforts, semiconductor enterprises can adeptly navigate the complexities of regulations. Furthermore, they can contribute to the development of a regulatory framework that fosters responsible innovation, equitable competition, and ensures a sustainable future for the industry. The journey towards shaping the future of semiconductors necessitates a concerted endeavor involving governments, industry magnates, and all pertinent stakeholders. With collaborative endeavors, we can ensure that this indispensable technology continues to propel progress and bestow benefits upon society at large.